概述
使用 oauth2 保护你的应用,可以分为简易的分为三个步骤:
配置资源服务器
配置认证服务器
配置 spring security
本文重点讲解接口对接中常使用的密码模式(以下简称 password 模式)和客户端模式(以下简称 client 模式)。授权码模式使用到了回调地址,是最为复杂的方式,通常网站中经常出现的微博,qq 第三方登录,都会采用这个形式。简化模式不常用。
项目准备
首先引入依赖:
<dependencies> <!-- 注意是starter,自动配置 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 不是starter,手动配置 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security.oauth</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-oauth2</artifactId> <version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- 将token存储在redis中 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>编写controller类,用来验证效果:
@RestController
@RestController
public class TestEndpoints {
/** 商品查询接口,后续不做安全限制 **/
@GetMapping("/product/{id}")
public String getProduct(@PathVariable String id) {
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
return "product id : " + id;
}
/** 订单查询接口,后续添加访问控制 **/
@GetMapping("/order/{id}")
public String getOrder(@PathVariable String id) {
Authentication authentication = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication();
return "order id : " + id;
}
}配置资源服务器和授权服务器
资源服务器和授权服务器都是OAuth2的核心内容,这里我们在一个配置类中进行配置。
为了简化开发,这里将客户端信息放到内存中,实际项目开发中可以配置到数据库中。
token的存储一般使用redis,一来性能较好,二是本身就有自动过期的机制,符合token的特性。
@Configuration
public class OAuth2ServerConfig {
private static final String DEMO_RESOURCE_ID = "order";
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
protected static class ResourceServerConfiguration extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) {
resources.resourceId(DEMO_RESOURCE_ID).stateless(true);
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
//配置order访问控制,必须认证过后才可以访问
.antMatchers("/order/**").authenticated();
}
}
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
protected static class AuthorizationServerConfiguration extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Autowired
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory;
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
String finalSecret = "{bcrypt}"+new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456");
//配置两个客户端,一个用于password认证一个用于client认证
clients.inMemory().withClient("client_1")
.resourceIds(DEMO_RESOURCE_ID)
.authorizedGrantTypes("client_credentials", "refresh_token")
.scopes("select")
.authorities("oauth2")
.secret(finalSecret)
.and().withClient("client_2")
.resourceIds(DEMO_RESOURCE_ID)
.authorizedGrantTypes("password", "refresh_token")
.scopes("select")
.authorities("oauth2")
.secret(finalSecret);
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) {
endpoints
.tokenStore(new RedisTokenStore(redisConnectionFactory))
.authenticationManager(authenticationManager)
.allowedTokenEndpointRequestMethods(HttpMethod.GET, HttpMethod.POST);
}
@Override
public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer oauthServer) {
//允许表单认证
oauthServer.allowFormAuthenticationForClients();
}
}
}认证思路:
- client 模式,没有用户的概念,直接与认证服务器交互,用配置中的客户端信息去申请 accessToken,客户端有自己的 client_id,client_secret ,对应于用户的 username,password,而客户端也拥有自己的 authorities,当采取 client 模式认证时,对应的权限也就是客户端自己的 authorities。
- password 模式,自己本身有一套用户体系,在认证时需要带上自己的用户名和密码,以及客户端的 client_id,client_secret。此时,accessToken 所包含的权限是用户本身的权限,而不是客户端的权限。
如果你的系统已经有了一套用户体系,每个用户也有了一定的权限,可以采用 password 模式;如果仅仅是接口的对接,不考虑用户,则可以使用 client 模式。
配置 spring security
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
@Override
protected UserDetailsService userDetailsService(){
BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
String finalPassword = "{bcrypt}"+bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("123456");
InMemoryUserDetailsManager manager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("user_1").password(finalPassword).authorities("USER").build());
manager.createUser(User.withUsername("user_2").password(finalPassword).authorities("USER").build());
return manager;
}
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){
return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
/**
* 这一步的配置是必不可少的,否则SpringBoot会自动配置一个AuthenticationManager,覆盖掉内存中的用户
*/
@Bean
@Override
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
AuthenticationManager manager = super.authenticationManagerBean();
return manager;
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.requestMatchers().anyRequest()
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/oauth/**").permitAll();
}
}重点就是配置了一个 UserDetailsService,和 ClientDetailsService 一样,为了方便运行,使用内存中的用户,实际项目中,一般使用的是数据库保存用户,具体的实现类可以使用 JdbcDaoImpl 或者 JdbcUserDetailsManager。
获取token
配置完成后,启动项目,使用Postman访问密码模式:
http://localhost:8080/oauth/token?username=user_1&password=123456&grant_type=password&scope=select&client_id=client_2&client_secret=123456响应如下: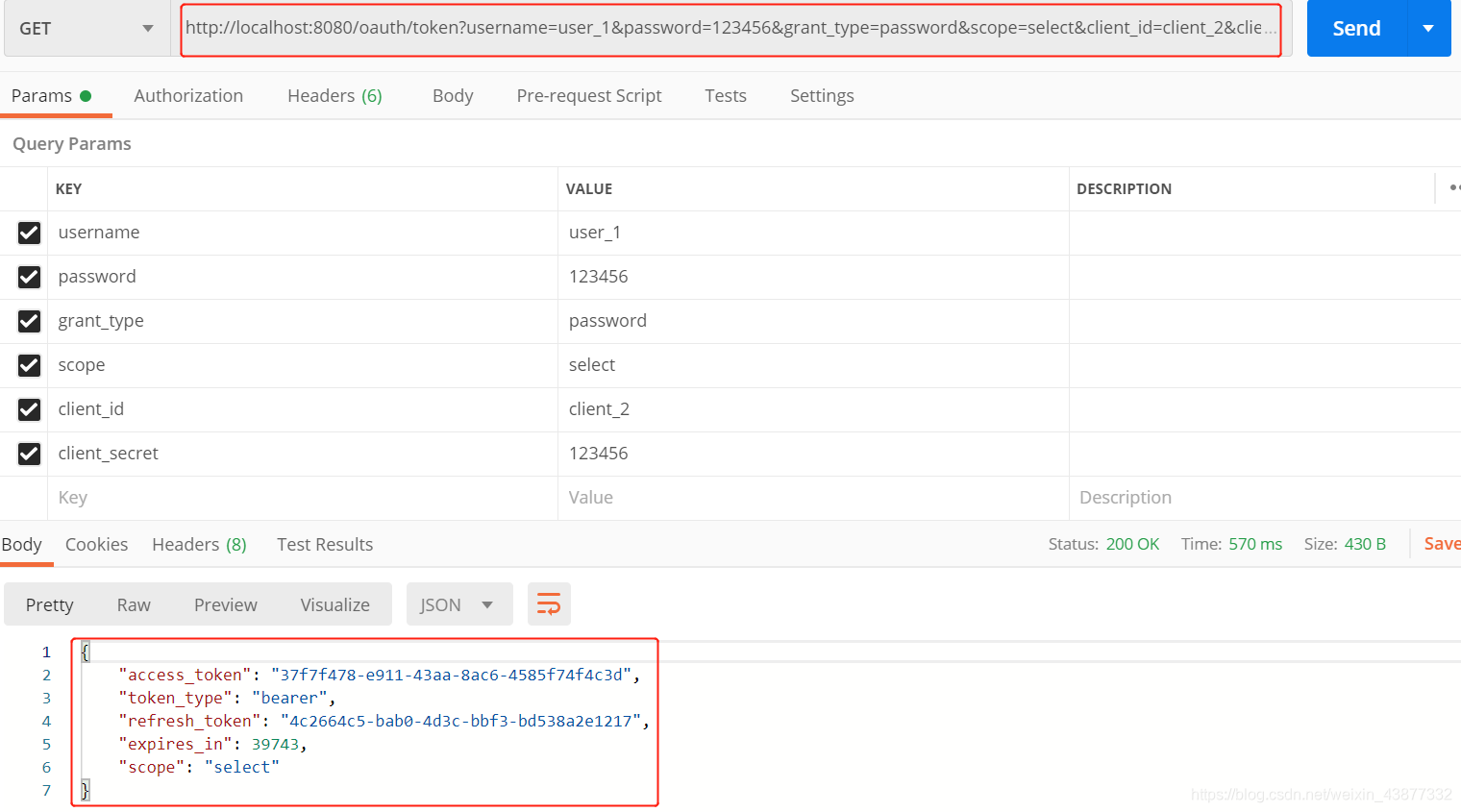
接下来试试客户端模式:
http://localhost:8080/oauth/token?grant_type=client_credentials&scope=select&client_id=client_1&client_secret=123456响应如下: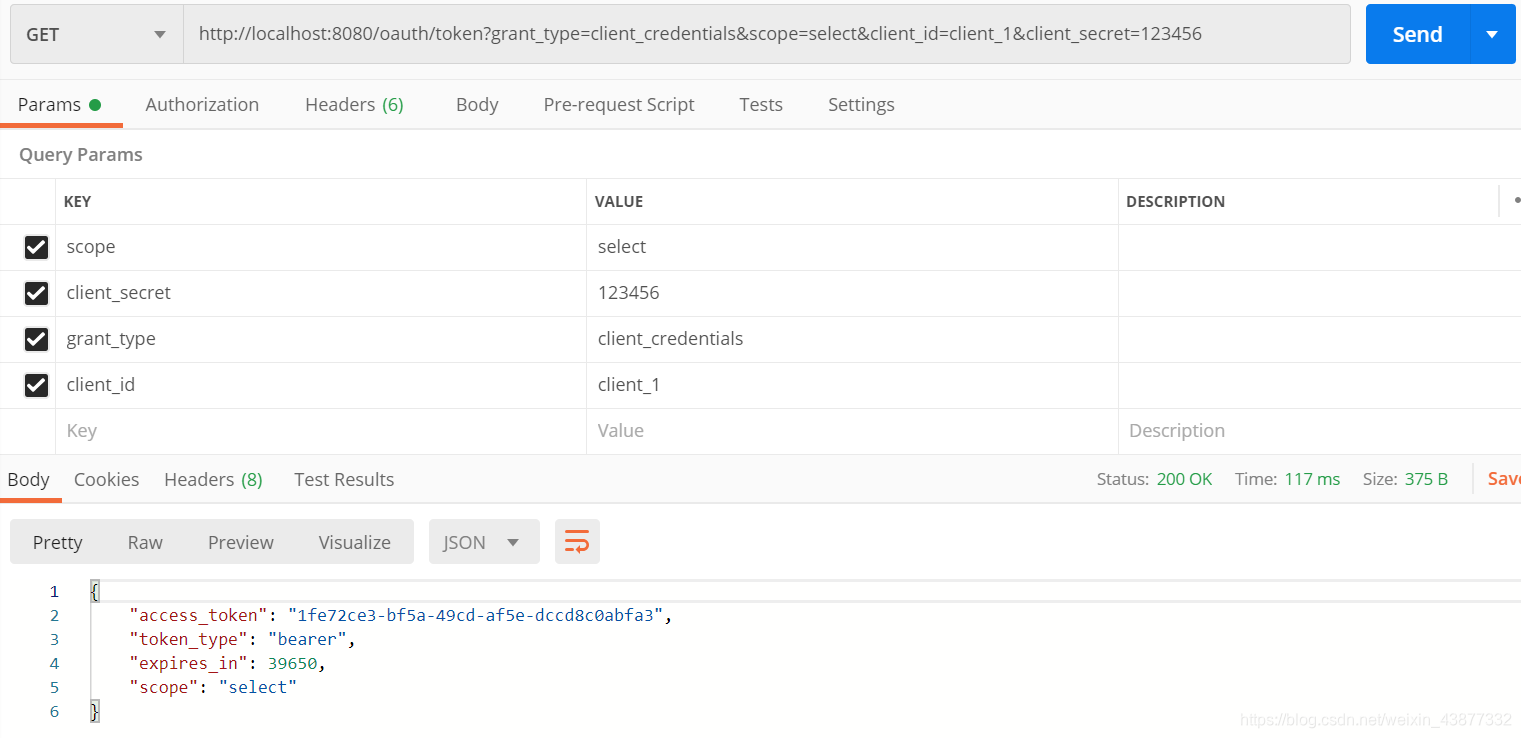
在配置中我们已经配置了对order资源的保护,测试如下:
而对于未受保护的product资源,访问效果如下:
接下来带有accessToken参数来访问受保护的order资源: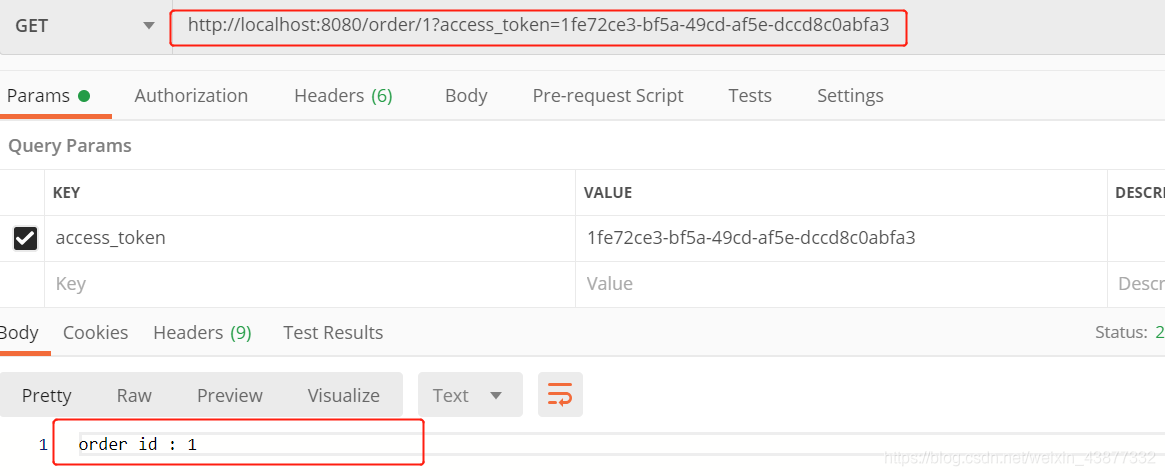
可以看到成功访问到了资源。
下面看下调试的情况:
密码模式下:
客户端模式下 :
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!