本文主要内容:
- 引导客户端和服务器
- 从Channel内引导客户端
- 添加ChannelHandler
- 使用ChannelOption和属性
Bootstrap类
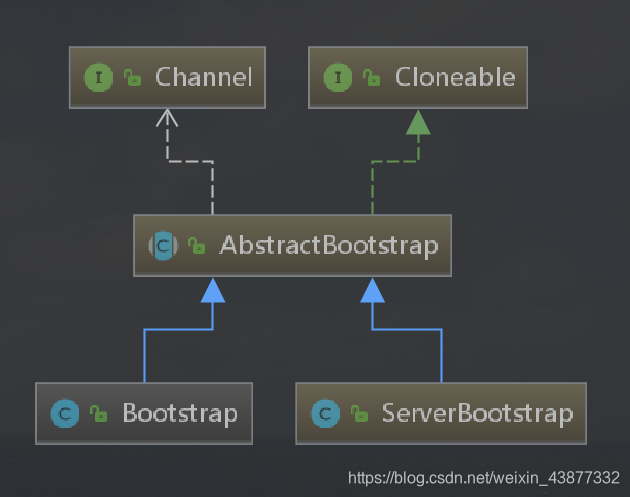
引导类的层次结构:
服务器致力于使用一个父Channel来接收来自客户端的连接,并创建子Channel以用于它们之间的通信;而客户端一般只需要一个单独的、没有父Channel的Channel来用于所有的网络交互。
首先聊聊为什么引导类是Cloneable的?
当我们需要创建多个具有类似配置或者完全相同配置的Channel的时候,可以通过在一个已经配置完成的引导类实例上调用clone()方法来返回另一个可以立即使用的引导类实例。
这种方式只会创建引导类实例的EventLoopGroup的一个浅拷贝,被浅拷贝的EventLoopGroup将在所有克隆的Channel实例之间共享。
引导客户端和无连接协议
Bootstrap类被用于客户端或者使用了无连接协议的应用程序中,主要方法有如下:
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| group | 设置 EventLoopGroup 用于处理所有的 Channel 的事件 |
| channel channelFactory | channel() 指定 Channel 的实现类。如果类没有提供一个默认的构造函数,你可以调用 channelFactory() 来指定一个工厂类被 bind() 调用。 |
| localAddress | 指定Channel应该绑定到本地地址 。如果不提供,将由操作系统创建一个随机的。或者,您可以使用 bind() 或 connect()指定localAddress |
| option | 设置 ChannelOption,其将被应用到新创建 Channel 的 ChannelConfig。这些选项将被 bind 或 connect 设置在Channel,这取决于哪个被首先调用。这个方法在创建Channel后没有影响。所支持 ChannelOption 取决于使用的Channel类型 |
| attr | 指定新创建的Channel属性值,这些属性值通过 bind 或 connect 设置在Channel,这取决于哪个被首先调用。这个方法在创建Channel后没有影响。所支持 ChannelOption 取决于使用的Channel类型 |
| handler | 设置添加到 ChannelPipeline 中的 ChannelHandler 接收事件通知。 |
| clone | 创建一个当前 Bootstrap的克隆拥有原来相同的设置。 |
| remoteAddress | 设置远程地址。此外,您可以通过 connect() 指定 |
| connect | 连接到远端,返回一个 ChannelFuture, 用于通知连接操作完成 |
| bind | 将通道绑定并返回一个 ChannelFuture,用于通知绑定操作完成后,必须调用 Channel.connect() 来建立连接。 |
引导客户端
引导过程如下图所示:

引导一个客户端代码如下:
public class BootstrapClient {
public static void main(String args[]) {
BootstrapClient client = new BootstrapClient();
client.bootstrap();
}
/**
* 代码清单 8-1 引导一个客户端
* */
public void bootstrap() {
//设置 EventLoopGroup,提供用于处理 Channel 事件的 EventLoop
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//创建一个Bootstrap类的实例以创建和连接新的客户端Channel
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
//指定要使用的Channel 实现
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
//设置用于 Channel 事件和数据的ChannelInboundHandler
.handler(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(
ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext,
ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Received data");
}
});
//连接到远程主机
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(
new InetSocketAddress("www.manning.com", 80));
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture)
throws Exception {
if (channelFuture.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println("Connection established");
} else {
System.err.println("Connection attempt failed");
channelFuture.cause().printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}Channel和EventLoopGroup的兼容性
在引导的过程中,在调用bind()或者connect()方法之前,必须调用一下方法来设置所需的组件:
- group()
- channel()或者channelFactory()
- handler()
如果不这样做,则将会导致IllegalStateException,尤其是handler()方法,因为它需要配置好的ChannelPipeline。
引导服务器
ServerBootstrap类
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| group | 设置ServerBootstrap要用的EventLoopGroup,这个 EventLoopGroup 提供 ServerChannel 的 I/O 处理并且接收 Channel |
| channel channelFactory | channel() 指定 Channel 的实现类。如果Channel没有提供一个默认的构造函数,你可以提供一个 ChannelFactory。 |
| localAddress | 指定 ServerChannel 应该绑定到的本地地址。如果不提供,将由操作系统创建一个随机的。或者,您可以使用 bind() 或 connect()指定localAddress |
| option | 指定一个 ChannelOption 来用于新创建的 ServerChannel 的 ChannelConfig 。这些选项将被设置在Channel的 bind() 或 connect(),这取决于谁首先被调用。在此调用这些方法之后设置或更改 ChannelOption 是无效的。 |
| childOption | 当Channel已被接受,指定一个 ChannelOption 应用于 Channel 的 ChannelConfig。 |
| attr | 指定 ServerChannel 的属性。这些属性可以被子Channel的 bind() 设置。当调用 bind() 之后,修改它们不会生效。 |
| childAttr | 应用属性到接收到的子Channel上。后续调用没有效果。 |
| handler | 设置添加到 ServerChannel 的 ChannelPipeline 中的 ChannelHandler。 |
| childHandler | 设置添加到接收到的 Channel 的 ChannelPipeline 中的 ChannelHandler。handler() 和 childHandler()之间的区别是前者是接收和处理ServerChannel,同时 childHandler() 添加处理器用于处理和接收 Channel。后者代表一个套接字绑定到一个远端。 |
| clone | 克隆 ServerBootstrap 用于连接到不同的远端,通过设置相同的原始 ServerBoostrap。 |
| bind | 绑定 ServerChannel 并且返回一个 ChannelFuture,用于通知连接操作完成了(结果可以是成功或者失败) |
引导服务器
ServerBootstrap类比Bootstrap类多了一些childXXX()方法,这是因为ServerChannel的实现负责创建子Channel,这些子Channel代表了已被接受的连接,用这些方法来简化将设置应用到已被接受的子Channel的ChannelConfig的任务。
下图展示了ServerBootstrap在bind()方法被调用时创建了一个ServerChannel,并且该ServerChannel管理了多个子Channel。

代码如下:
public void bootstrap() {
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//创建 Server Bootstrap
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//设置 EventLoopGroup,其提供了用于处理 Channel 事件的EventLoop
bootstrap.group(group)
//指定要使用的 Channel 实现
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//设置用于处理已被接受的子 Channel 的I/O及数据的 ChannelInboundHandler
.childHandler(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext,
ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Received data");
}
});
//通过配置好的 ServerBootstrap 的实例绑定该 Channel
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture)
throws Exception {
if (channelFuture.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println("Server bound");
} else {
System.err.println("Bind attempt failed");
channelFuture.cause().printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}从Channel引导客户端
在实际项目开发中有时需要从已经被接受的子Channel中引导一个客户端Channel,我们可以创建一个新的Bootstrap实例,但是这样会产生额外的线程,以及在已被接受的子Channel和客户端Channel之间交换数据时带来的上下文切换。
一个更好的解决方案是:通过将已被接受的子Channel的EventLoop传递给Bootstrap的group()方法来共享该EventLoop。

代码实现如下:
public void bootstrap() {
//创建 ServerBootstrap 以创建 ServerSocketChannel,并绑定它
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//设置 EventLoopGroup,其将提供用以处理 Channel 事件的 EventLoop
bootstrap.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(), new NioEventLoopGroup())
//指定要使用的 Channel 实现
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//设置用于处理已被接受的子 Channel 的 I/O 和数据的 ChannelInboundHandler
.childHandler(
new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() {
ChannelFuture connectFuture;
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx)
throws Exception {
//创建一个 Bootstrap 类的实例以连接到远程主机
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
//指定 Channel 的实现
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(
//为入站 I/O 设置 ChannelInboundHandler
new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(
ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in)
throws Exception {
System.out.println("Received data");
}
});
//使用与分配给已被接受的子Channel相同的EventLoop
bootstrap.group(ctx.channel().eventLoop());
connectFuture = bootstrap.connect(
//连接到远程节点
new InetSocketAddress("www.manning.com", 80));
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(
ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext,
ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
if (connectFuture.isDone()) {
//当连接完成时,执行一些数据操作(如代理)
// do something with the data
}
}
});
//通过配置好的 ServerBootstrap 绑定该 ServerSocketChannel
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture)
throws Exception {
if (channelFuture.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println("Server bound");
} else {
System.err.println("Bind attempt failed");
channelFuture.cause().printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}编写Netty应用程序的一个一般原则:尽可能地重用EventLoop,以减少线程创建所带来的开销。
在引导过程中添加多个ChannelHandler
之前的代码中,我们调用handler()或者childHandler()方法来添加单个的ChannelHandler。Netty提供了一个特殊的ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter()子类:
public abstract class ChannelInitializer<C extends Channel> extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter通过它的protected abstract void initChannel(C ch) throws Exception方法来讲多个ChannelHandler添加到一个ChannelPipeLine中的简便方法。你只需要简单的向Bootstrap或ServerBootstrap的实例提供你的ChannelInitializer实现即可,在该方法返回之后,ChannelInitializer的实例将会从ChannelPipeline中移除它自己。
public void bootstrap() throws InterruptedException {
//创建 ServerBootstrap 以创建和绑定新的 Channel
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//设置 EventLoopGroup,其将提供用以处理 Channel 事件的 EventLoop
bootstrap.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(), new NioEventLoopGroup())
//指定 Channel 的实现
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
//注册一个 ChannelInitializerImpl 的实例来设置 ChannelPipeline
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializerImpl());
//绑定到地址
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));
future.sync();
}
//用以设置 ChannelPipeline 的自定义 ChannelInitializerImpl 实现
final class ChannelInitializerImpl extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> {
@Override
//将所需的 ChannelHandler 添加到 ChannelPipeline
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new HttpClientCodec());
pipeline.addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
}
}如果你的应用程序使用了多个ChannelHandler,自己定义一个ChannelInitializer的实现来将它们安装到ChannelPipeline中即可。
使用Netty的ChannelOption和属性
在每个Channel创建时都手动配置它很麻烦,这时我们可以通过option()方法来讲ChannelOption应用到引导,我们提供的值将会被自动应用到引导所创建的所有Channel。
Netty提供了AttributeMap抽象以及AttributeKey等工具来实现任何类型的数据项与客户端和服务器Channel之间安全地关联。
下面代码展示了如何使用ChannelOption来配置Channel,以及如何使用属性来存储整型值。
public void bootstrap() {
//创建一个 AttributeKey 以标识该属性
final AttributeKey<Integer> id = AttributeKey.newInstance("ID");
//创建一个 Bootstrap 类的实例以创建客户端 Channel 并连接它们
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
//设置 EventLoopGroup,其提供了用于处理 Channel 事件的 EventLoop
bootstrap.group(new NioEventLoopGroup())
//指定 Channel 的实现
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(
//设置用以处理 Channel 的 I/O 以及数据的 ChannelInboundHandler
new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() {
@Override
public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx)
throws Exception {
//使用 AttributeKey 检索属性以及它的值
Integer idValue = ctx.channel().attr(id).get();
// do something with the idValue
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(
ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext,
ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Received data");
}
}
);
//设置 ChannelOption,其将在 connect()或者bind()方法被调用时被设置到已经创建的 Channel 上
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000);
//存储该 id 属性
bootstrap.attr(id, 123456);
//使用配置好的 Bootstrap 实例连接到远程主机
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(
new InetSocketAddress("www.manning.com", 80));
future.syncUninterruptibly();
}引导DatagramChannel
前面提到的都是基于TCP协议的SocketChannel,但是Bootstrap类也可以被用于无连接的协议,Netty提供了各种DatagramChannel的实现,唯一区别就是,不再调用connect()方法,而是只调用bind()方法,代码如下:
public void bootstrap() {
//创建一个 Bootstrap 的实例以创建和绑定新的数据报 Channel
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
//设置 EventLoopGroup,其提供了用以处理 Channel 事件的 EventLoop
bootstrap.group(new OioEventLoopGroup()).channel(
//指定 Channel 的实现
OioDatagramChannel.class).handler(
//设置用以处理 Channel 的 I/O 以及数据的 ChannelInboundHandler
new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<DatagramPacket>() {
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,
DatagramPacket msg) throws Exception {
// Do something with the packet
}
}
);
//调用 bind() 方法,因为该协议是无连接的
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress(0));
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture channelFuture)
throws Exception {
if (channelFuture.isSuccess()) {
System.out.println("Channel bound");
} else {
System.err.println("Bind attempt failed");
channelFuture.cause().printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}关闭
最重要的是关闭EventLoopGroup,通过调用EventLoopGroup.shutdownGracefully()方法。这个调用将返回一个 Future 用来通知关闭完成。注意,shutdownGracefully()也是一个异步操作,所以你需要阻塞,直到它完成或注册一个侦听器直到返回的 Future 来通知完成。
public void bootstrap() {
//创建处理 I/O 的EventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//创建一个 Bootstrap 类的实例并配置它
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
//...
.handler(
new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() {
@Override
protected void channelRead0(
ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext,
ByteBuf byteBuf) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Received data");
}
}
);
bootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress("www.manning.com", 80)).syncUninterruptibly();
//,,,
//shutdownGracefully()方法将释放所有的资源,并且关闭所有的当前正在使用中的 Channel
Future<?> future = group.shutdownGracefully();
// block until the group has shutdown
future.syncUninterruptibly();
}本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!